VIDEO PHOTOS AND INFORMATION
What you have been waiting for…
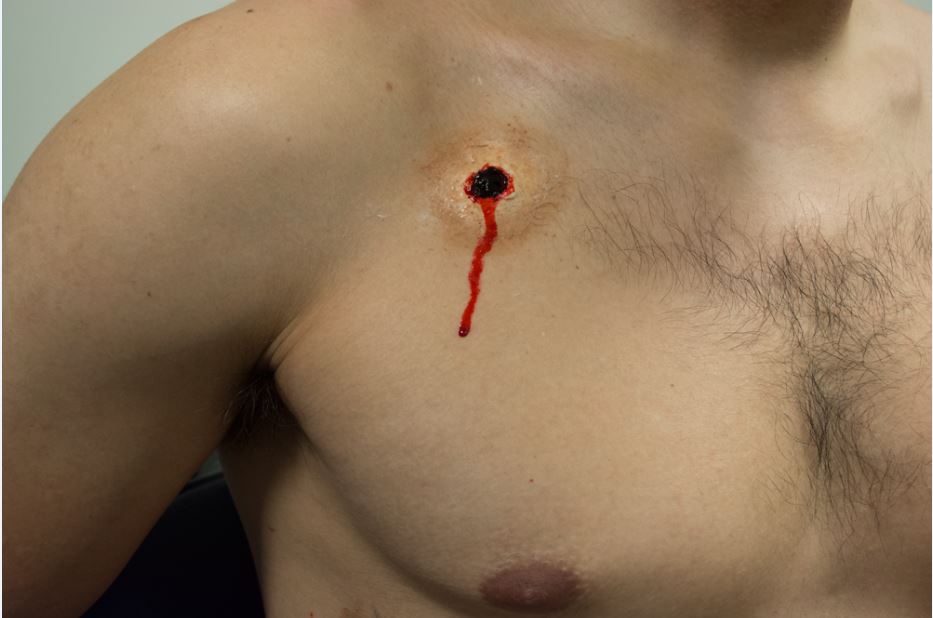
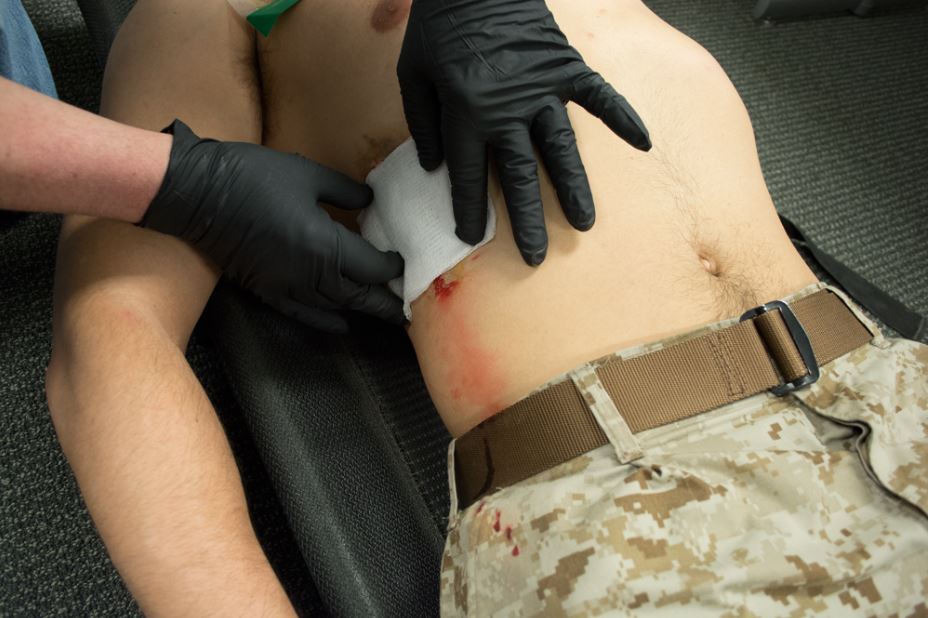
Identify a penetrating wound in the thoracic region. The wound should not be presenting blood or exudate if so a (CWS)6™ should be used to occlude and secure the site
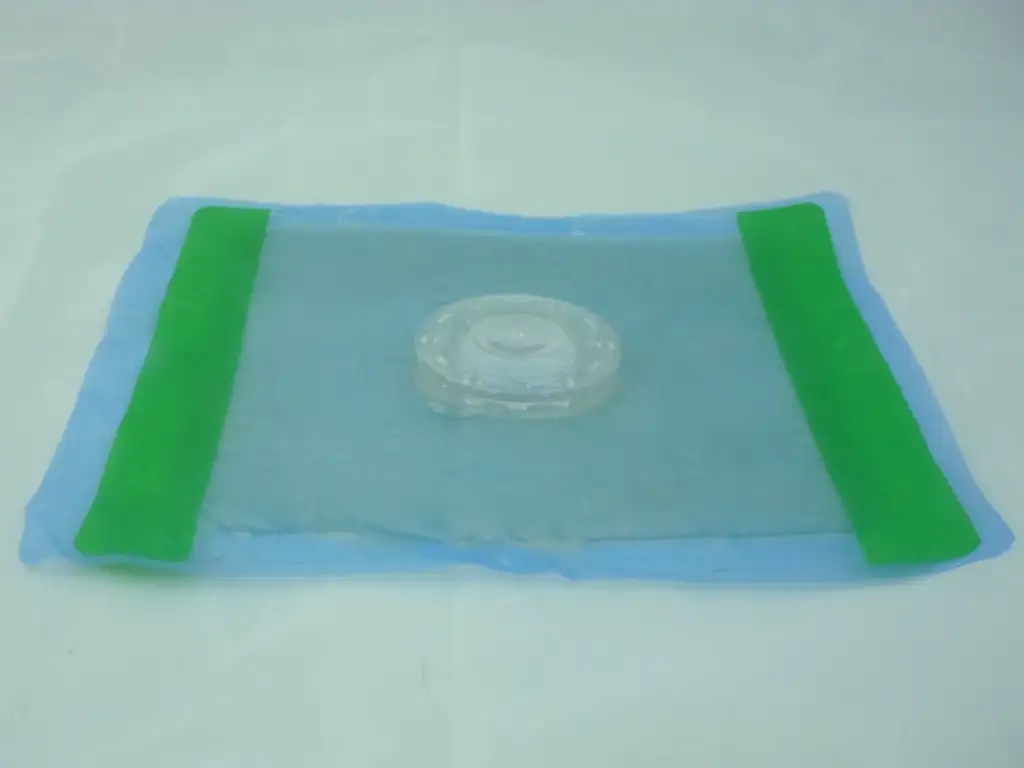
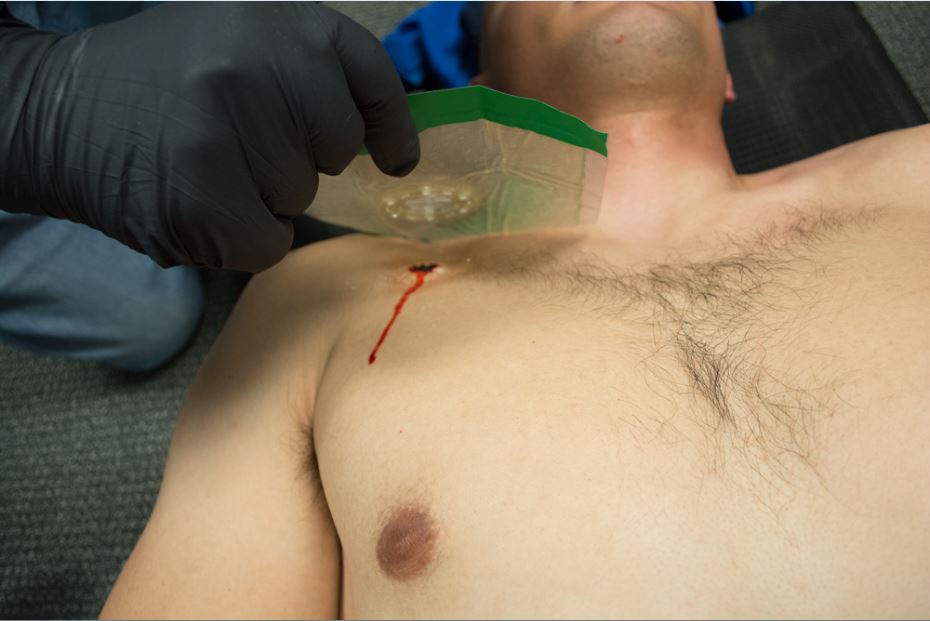
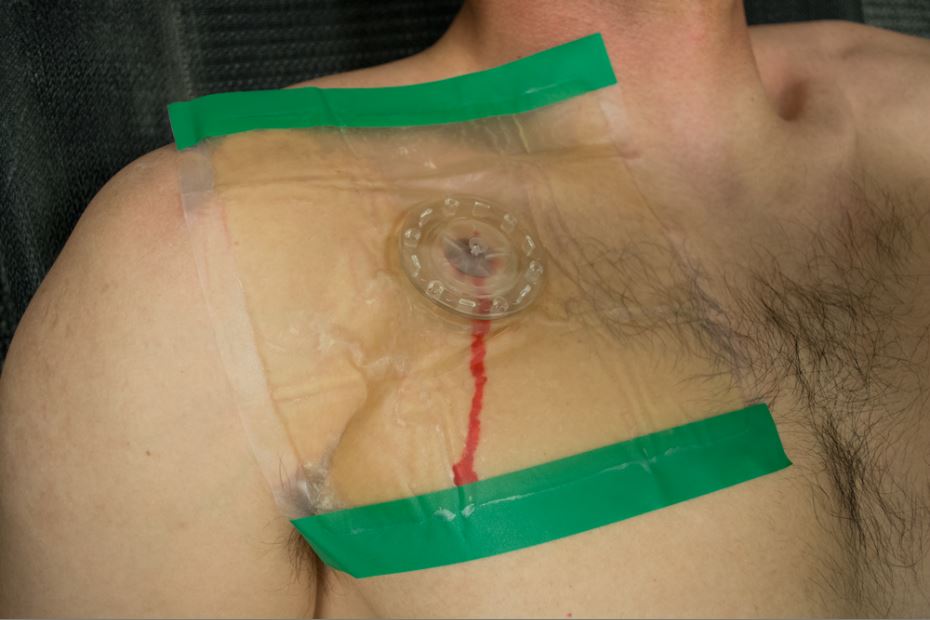
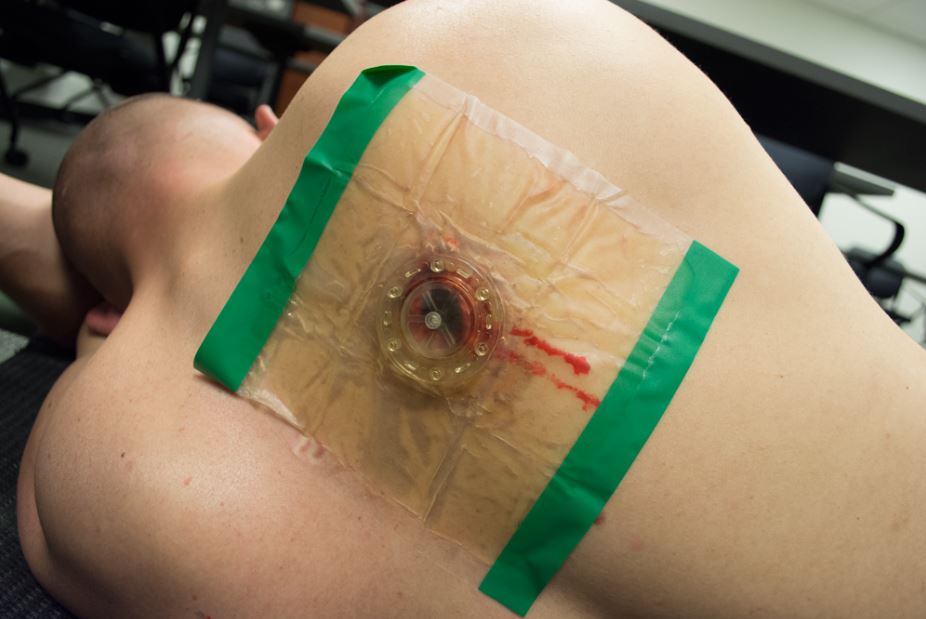
Center the valve directly over the wound and ensure a complete (occlusive) seal all the way around; observe proper valve fluctuation when breathing in and out allowing you to quickly move on to the next wound or patient
Identify additional entry or exit wounds
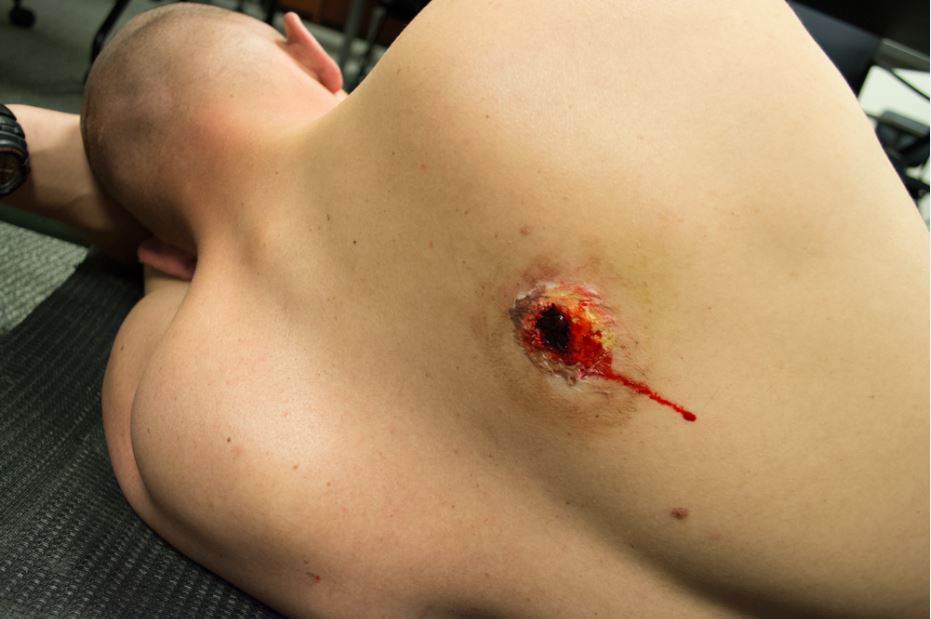
Ideally all thoracic wounds should be managed with the (FTS)® product since it is unknown which may cause a tension pneumothorax
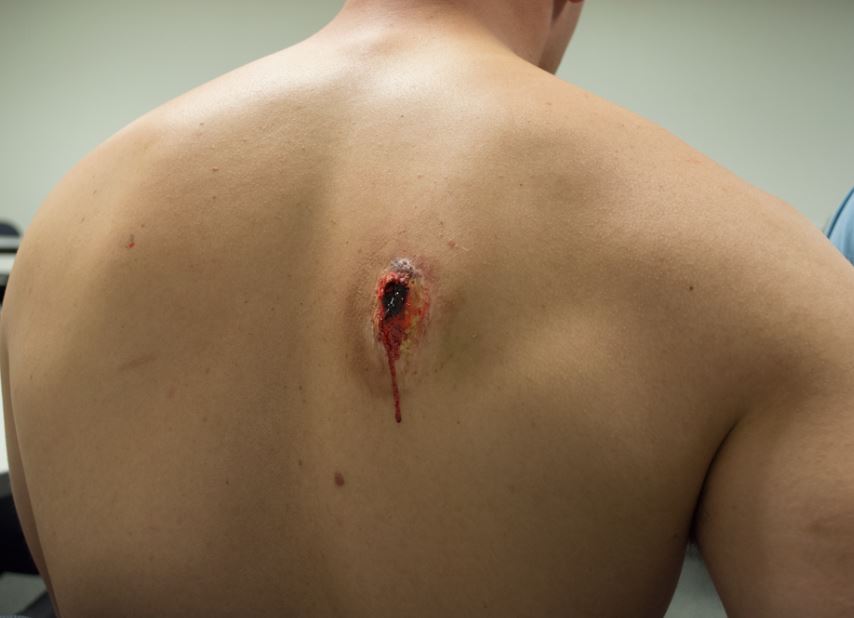
the (FTS)® product can be effectively utilized in any area of the thoracic region since the patented hardened valve cage allows it to function even if covered
Wounds in the thoracic region that may be too extensive for the (FTS)® should be occluded with the (CWS)6™ product covering a gauze type dressing
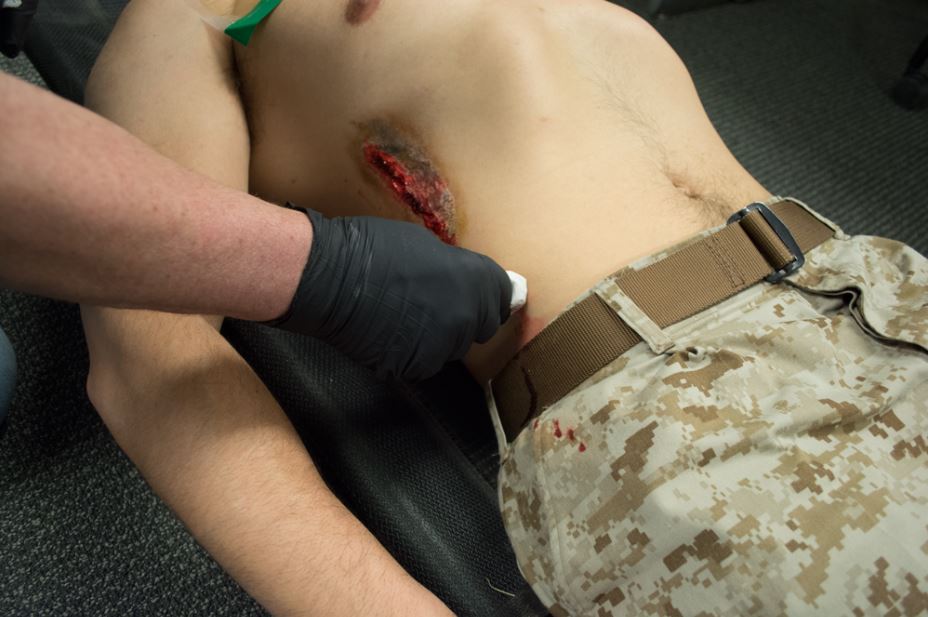
Wounds anywhere in the body can be quickly bandaged and secured with (CWS)6™
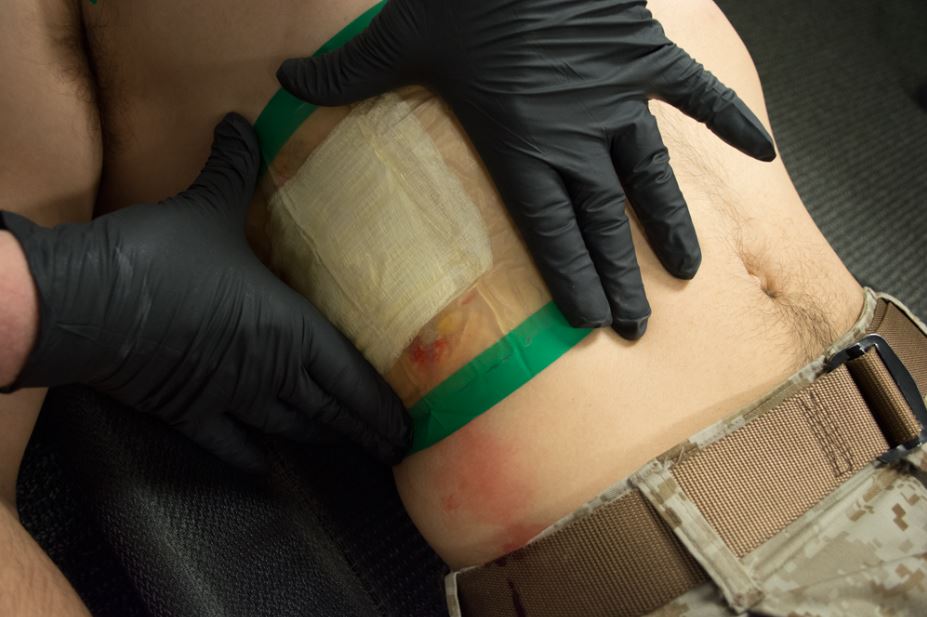
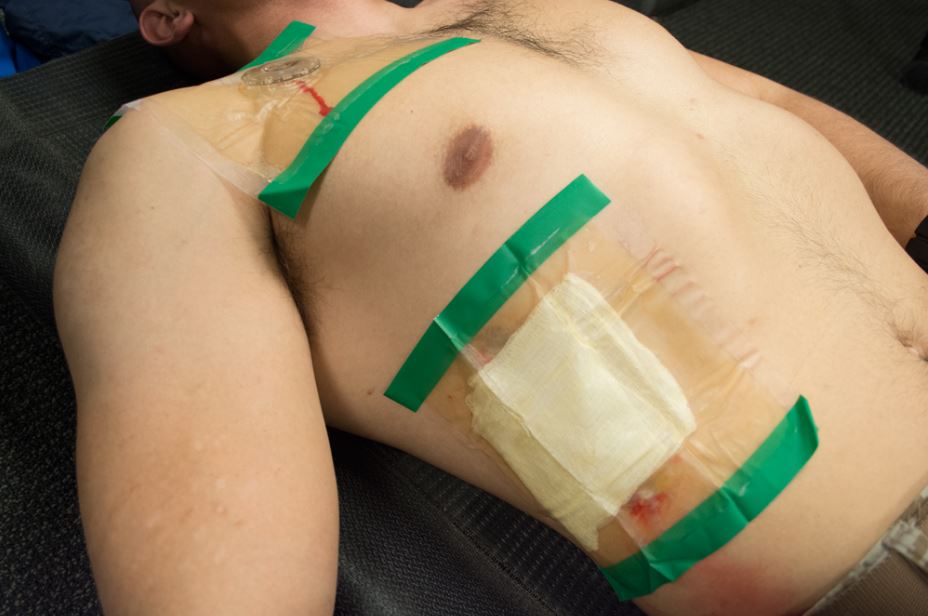
(CWS)6™ / (PWS)6™ as well as (CWS)6/10™ / (PWS)6/10™ can be used to protect surgical sites or wound sites for showering or bathing
(IPA)™ and (IPA)R™ [shown] will seal and secure an IV site from contamination and accidental dislodgement
